IntroductionYou grab a bottle of water from the shelf, twist it in your hand, and notice a small tri...
How To Choose The Right Material For Plastic Injection Molding(ABS、PP、PE、PC、PA、PBT)

Choosing the right material for plastic injection molding is one of the most important factors that determine the performance, durability, cost, and manufacturability of your parts. Whether you are developing consumer electronics, automotive connectors, medical devices, industrial components, or household products, selecting the correct injection molding material ensures both production efficiency and long-term reliability.
This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the most common polymers used in injection molding, their properties, advantages, limitations, and typical applications. We also offer a practical step-by-step framework to help you decide the best plastic for your project.
Why Material Selection Is Critical in Injection Molding
Injection molding is a high-efficiency mass production process, but the success of each molded part relies heavily on the chosen resin. The right material improves:
Mechanical performance — strength, impact resistance, fatigue life
Thermal stability — ability to withstand temperature without deformation
Chemical resistance — durability against oils, detergents, fuels, and solvents
Dimensional stability — maintaining tight tolerances during long-term use
Surface appearance — gloss, matte finish, transparency, color stability
Production efficiency — cycle time, flowability, shrinkage rate
Cost optimization — material cost + processing cost + mold complexity
This is why proper injection molding material selection is essential for any engineering or manufacturing team.
Mechanical Strength Requirements
Do the parts need to handle load or impact?
Will they bend repeatedly?
Do they require long-term structural stability?
Examples:
high strength: Nylon (PA6 / PA66), PC, PBT
high impact: ABS, PC-ABS, HDPE
flexibility: PP, TPU, TPE
Heat Resistance
Parts exposed to temperature need a polymer with high thermal stability.
120–150°C: Nylon 66, PC, PBT
150–250°C: PPS, PSU
250°C+: PEEK, PEI
Applications include automotive under-hood components, lighting fixtures, and industrial tools.
Heat stability also affects mold temperature, cooling time, and cycle cost.
Chemical Resistance
If parts contact oils, fuels, alcohol, detergents, or cleaning fluids, chemical resistance is essential.
Excellent resistance: PP, HDPE, POM, PTFE, PPS
Moderate: ABS, PC, Nylon
Weak: Acrylic (PMMA)
Chemical compatibility prevents cracking, swelling, or degradation.
Environmental Conditions
Will the part be used outdoors?
Is UV resistance required?
Will humidity or water absorption affect it?
Materials for outdoor use:
ASA → excellent UV resistance
PC → impact resistant + UV-stabilized versions available
PMMA → superior weatherability
For high humidity:
Avoid Nylon unless modified, because it absorbs moisture
Surface Appearance Requirements
If your product is consumer-facing, appearance matters.
High gloss: ABS, PMMA
Matte and textured finishes: PC-ABS, PP
Crystal clear transparency: PMMA, PC
This is crucial in electronics housings, cosmetic packaging, and home appliances.
Regulatory or Safety Requirements
Depending on the application, materials may need additional certification:
FDA / food grade: PP, HDPE, Tritan, medical-grade TPE
UL flame-retardant: FR-ABS, FR-PC, FR-PA
Medical ISO 10993: PC, PP, TPE
Materials must fit compliance standards beyond engineering properties.
Cost and Production Efficiency
Cost consists of:
resin price
molding temperature (energy consumption)
cycle time
scrap rate
mold complexity
Low-cost, easy-to-process materials:
PP, PE, ABS
Higher-cost engineering materials:
PC, Nylon, PBT
Premium high-performance materials:
PEEK, PPS, PSU
Detailed Comparison of Common Injection Molding Materials
Below is an in-depth examination of the most commonly used plastics for injection-molded parts.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Key Features
High impact resistance
Easy processing
Good surface finish
Suitable for plating and painting
Applications
Electronics housings
Automotive interior parts
Toys (e.g., LEGO)
Appliance panels
Why choose ABS for injection molding?
It offers an excellent balance of strength, appearance, and cost.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Features
Lightweight
Chemical resistant
Food-safe grades available
Excellent fatigue resistance (living hinges)
Applications
Food containers
Medical syringes
Hinged caps
Automotive components
PP is one of the most cost-effective and versatile plastics in injection molding.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Key Features
Extremely high impact strength
Transparent
Heat resistant
Good dimensional stability
Applications
Lighting lenses
Safety goggles
Transparent guards
Electronics casings
PC is ideal for protective or transparent components.
Nylon (PA6, PA66)
Key Features
High strength and toughness
Excellent wear resistance
High heat stability
Good chemical resistance
Applications
Gears
Bearings
Automotive engine parts
Industrial components
Nylon is preferred for structural and load-bearing parts.
POM (Polyoxymethylene / Acetal)
Key Features
Low friction
High stiffness
Dimensional stability
Excellent for precision parts
Applications
Gears
Valves
Connectors
Mechanical motion components
Ideal for high-precision components requiring minimal friction.
PMMA (Acrylic)
Key Features
Crystal clear transparency
UV resistant
High aesthetic quality
Applications
Display panels
Automotive lighting
Optical components
PMMA is the best alternative to glass for lightweight optical clarity.
Elastomers (TPE / TPU)
Key Features
Flexible
Soft-touch feel
Durable
Ideal for overmolding
Applications
Tool grips
Wearables
Seals and gaskets
Medical devices
Elastomers enhance ergonomics and sealing performance.
High-Performance Engineering Plastics
Used in extreme environments where standard plastics fail.
PEEK
Withstands 250°C+
Superior mechanical strength
Chemical and radiation resistant
Applications: aerospace, medical implants, oil & gas tools
PPS
Exceptionally heat resistant
Flame retardant
Excellent dimensional stability
Applications: automotive electronics, sensors
PSU / PES
High temperature resilience
Hydrolysis resistant
Applications: food equipment, medical sterilizationThese materials are expensive but irreplaceable in demanding applications.
Step-by-Step Framework for Selecting the Best Injection Molding Material
To simplify decision-making, follow this engineering checklist:
Step 1: Define Mechanical Requirements
Strength? Impact? Flexibility?
→ Choose ABS / PC / Nylon / PP / TPE based on needs.
Step 2: Evaluate Environmental Conditions
Heat? UV? Moisture? Chemicals?
→ PC, ASA, Nylon, PEEK, PP depending on exposure.
Step 3: Determine Aesthetic Expectations
Glossy? Matte? Transparent?
→ ABS, PMMA, PC.
Step 4: Consider Regulatory Compliance
Food-grade? Flame retardant? Medical?
→ PP, HDPE, FR-PC, TPE, medical resins.
Step 5: Balance Material Cost vs. Performance
If cost is critical → PP, ABS
If performance is vital → PC, Nylon
If extreme environments → PEEK, PPS
Material Testing Before Mass Production
Before finalizing your material, consider:
Mold flow analysis (SIMULATION)
Shrinkage and warpage tests
Prototype molding trial
Mechanical performance tests
Chemical compatibility assessments
This ensures the material meets all functional and production requirements.
Conclusion
Selecting the right material for plastic injection molding is a critical engineering decision that affects durability, cost, efficiency, aesthetics, and long-term product success. By understanding key polymer properties and using a systematic evaluation framework, manufacturers can confidently choose the ideal plastic for any application—from cost-effective consumer products to high-performance industrial components.
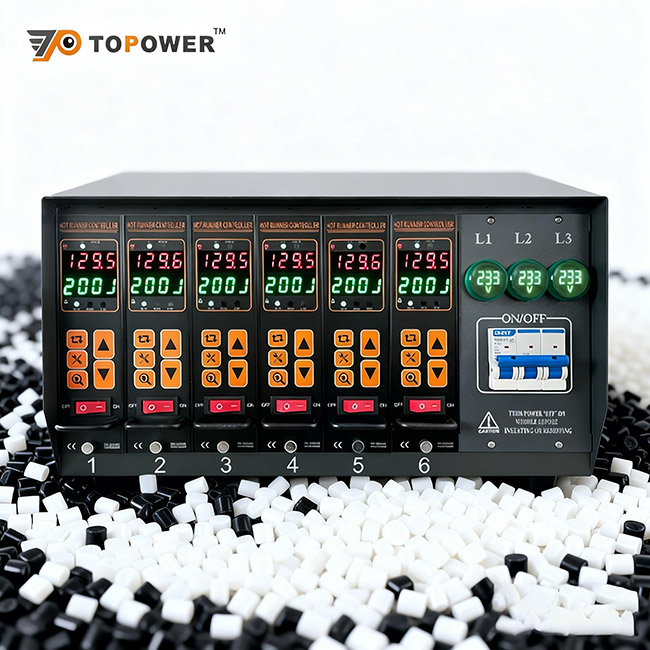
Improve Your Injection Molding Consistency with Smarter Temperature Control
Material selection matters—but without stable melt temperature, even the best resin can fail.
Our hot runner temperature controllers deliver precise, closed-loop control for ABS, PC, Nylon, PBT, POM, and high-performance polymers, ensuring uniform flow, fewer defects, and shorter startup time.
If you're looking to boost molding efficiency and part performance, let’s connect—we help manufacturers achieve repeatable, high-quality production every day.
Learn more: https://www.cntopower.com/HotRunnerTemperatureController/