IntroductionYou grab a bottle of water from the shelf, twist it in your hand, and notice a small tri...
Understanding Heat Resistant Plastic: Types, Applications, and Performance Comparison
Introduction to Heat Resistant Plastic
When it comes to manufacturing components that must withstand high operating temperatures, heat resistant plastic offers a reliable and lightweight solution. Unlike conventional plastics that deform or lose strength under heat, heat resistant materials are engineered to perform in environments above 150°C — and sometimes beyond 300°C.
From automotive parts and electrical housings to industrial machinery and kitchen appliances, these materials have become indispensable across industries seeking durability, performance, and design flexibility.
At CNTOPower, we understand how temperature stability directly impacts the efficiency and lifespan of molded components. That’s why we provide reliable control systems and precise temperature management solutions to help manufacturers maximize the performance of their heat resistant plastic applications.
What Makes a Plastic Heat Resistant?
The temperature tolerance of heat resistant plastic depends mainly on its molecular structure and the presence of reinforcing additives. Polymers with strong intermolecular bonds, aromatic rings, or crystalline regions resist softening at elevated temperatures.
Manufacturers often enhance heat resistance through glass fiber reinforcement or heat stabilizers, which further improve dimensional stability and mechanical strength under heat stress.
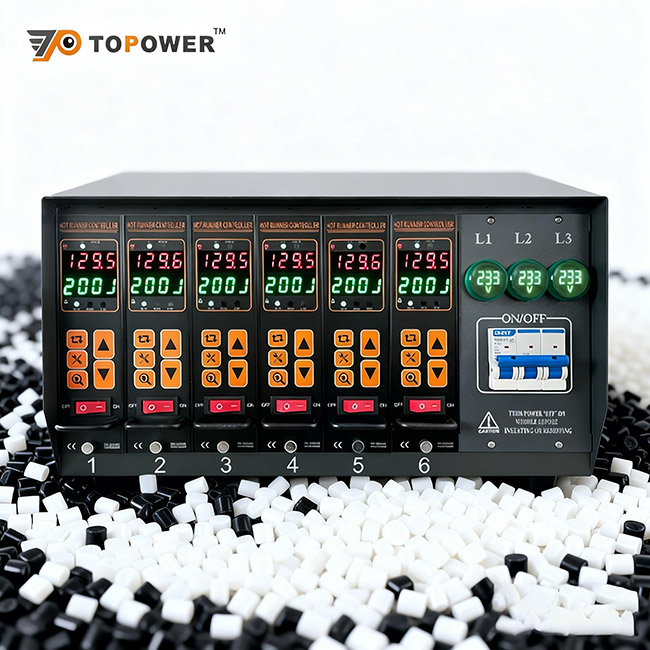
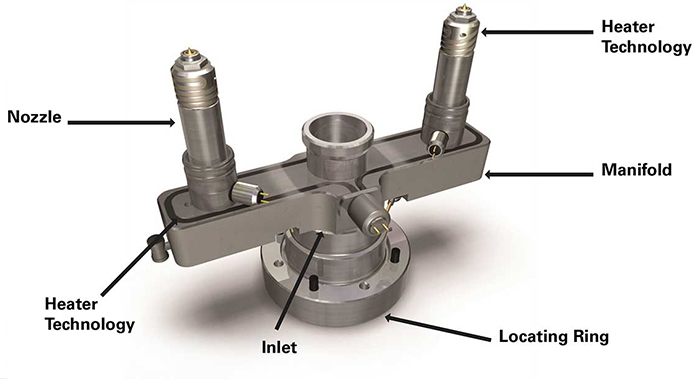
For engineers and designers, understanding a material’s Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) and Melting Point (Tm) is essential when selecting the right polymer for a specific high-temperature application. Accurate temperature control during processing is critical — and that’s where CNTOPower Hot Runner Temperature Controllers deliver precision and consistency.
Common Types of Heat Resistant Plastic Materials
There are many high temperature resistant plastic types available today, each offering unique properties for specialized applications.
Among them, the five most heat resistant plastics stand out for their exceptional thermal and mechanical stability:
Polyetherimide (PEI)
PEI can withstand continuous use temperatures up to 340°C. It offers high strength, dimensional stability, and flame resistance, making it suitable for aircraft interiors, medical devices, and electrical components.
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
PEEK is one of the best-known heat resistant engineering plastics, operating up to 250°C continuously and maintaining excellent strength and chemical resistance. It’s widely used in aerospace, automotive, and oil & gas industries.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Known under the brand name Teflon, PTFE has a continuous service temperature around 260°C and outstanding chemical inertness. It is perfect for gaskets, seals, and non-stick coatings that face both heat and chemical exposure.
Polybenzimidazole (PBI)
PBI offers the highest heat resistance of any thermoplastic, maintaining strength beyond 400°C. It’s used in aerospace insulation, defense applications, and high-performance bearings.
Polydicyclopentadiene (pDCPD)
This innovative thermoset plastic offers superior thermal stability and impact resistance, making it ideal for automotive body panels, industrial housings, and chemical equipment that face heat and mechanical stress simultaneously.
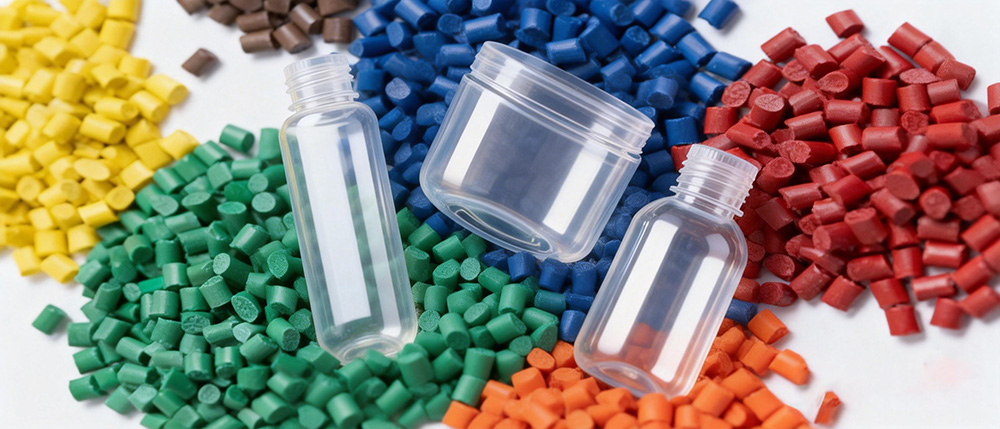
Other materials, such as Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), Polysulfone (PSU), Polyimide (PI), and Nylon (PA), are also valuable options, offering a balance between cost, strength, and processing ease for both industrial and consumer applications.
These materials enable engineers to replace metals in various applications, reducing weight while maintaining or even enhancing thermal and chemical performance.

Best Heat Resistant Plastic for Different Applications
Choosing the right material depends on the temperature range, exposure duration, and environment. Here’s how different industries use them:
Automotive Industry
In modern vehicles, heat resistant plastic for automotive parts replaces metal in areas like air intake manifolds, under-hood covers, and sensor housings. PPS and PEEK are particularly popular due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and heat stability.
Kitchen and Home Appliances
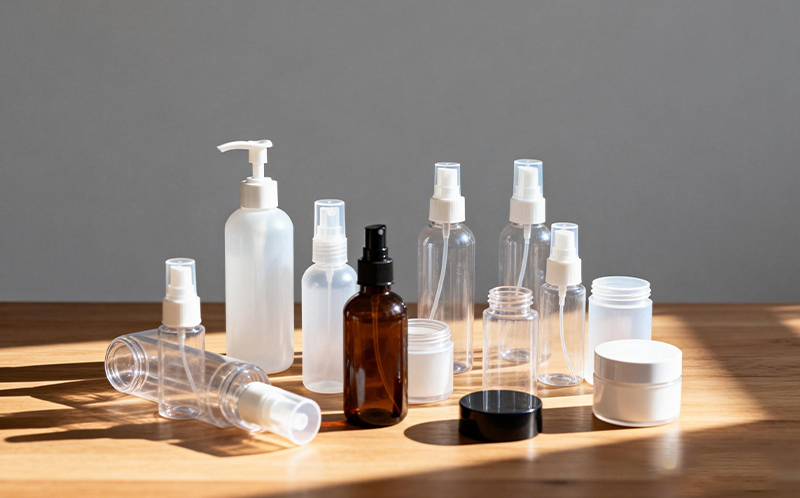
Appliances such as coffee makers, air fryers, and ovens demand heat resistant plastic for kitchen appliances that can endure repeated heating cycles without degrading. Materials like PC and PSU are commonly used here.
Industrial and Manufacturing Equipment
Factories often require heat resistant plastic materials for gears, seals, and housings that must resist both heat and friction. PEEK and PPS again stand out for their ability to maintain stiffness under continuous stress.
In each of these cases, heat resistant plastic vs metal comparison often reveals that plastics deliver superior design flexibility, corrosion resistance, and overall cost-effectiveness — especially when processed with stable thermal control systems like those from CNTOPower.
Heat Resistant Plastic Sheets and Components
Heat resistant plastic sheets for industrial use are often fabricated into guards, panels, and transparent shields where exposure to heat is unavoidable. Polycarbonate sheets, for example, combine clarity with impact and temperature resistance, making them ideal for enclosures or machine covers.
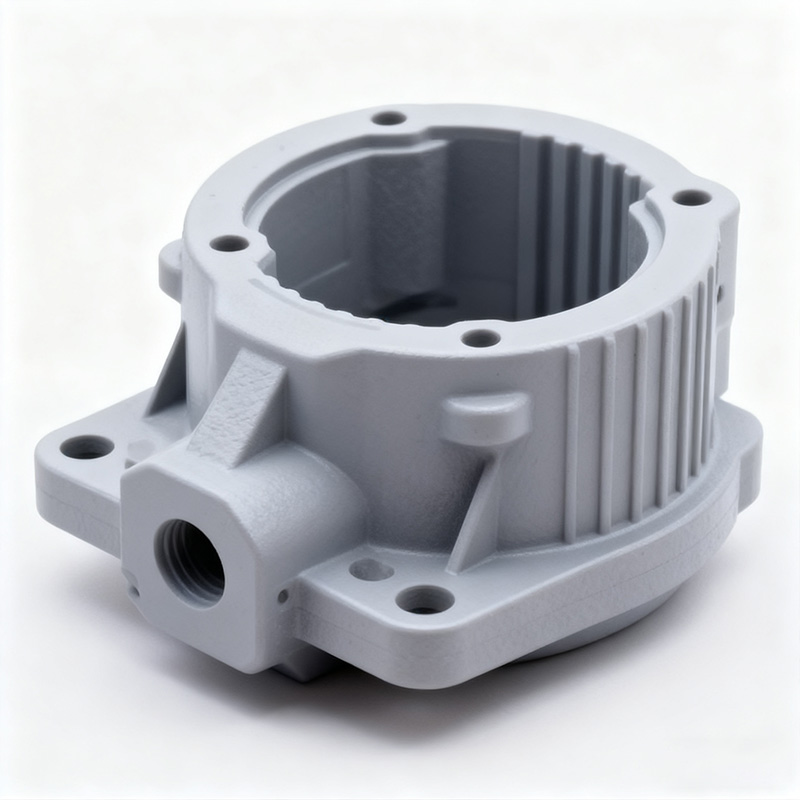
For specialized needs, manufacturers can produce custom heat resistant plastic components, tailored to specific shapes, tolerances, and performance requirements. Customization enables seamless integration into complex systems across industries like food processing, semiconductors, and cleanroom equipment.
Heat Resistant Plastic in Injection Molding
In the world of precision manufacturing, heat resistant plastic molding materials play a vital role. However, these high-performance polymers often require special injection molding conditions — such as higher melt temperatures and reinforced molds — to achieve optimal performance.
This makes accurate temperature control essential for achieving consistent product quality. With CNTOPower Hot Runner Temperature Controllers, molders can precisely regulate each heating zone, ensuring uniform flow, reducing material stress, and extending mold life — even when processing advanced engineering plastics.
How to Choose the Right Heat Resistant Plastic for Your Project
Selecting the ideal material starts with identifying key requirements:
Operating Temperature: Define the maximum exposure temperature and duration.
Mechanical Load: Evaluate tensile, flexural, and impact strength under heat.
Chemical Exposure: Consider resistance to oils, fuels, and cleaning agents.
Cost Efficiency: Balance performance with manufacturing cost.
Forming Process: Confirm compatibility with your molding or machining methods.
At CNTOPower, we help manufacturers integrate high-performance materials with smart temperature control technology. Whether you are working with high temperature resistant plastic or standard thermoplastics, our systems help you achieve consistent results, minimize scrap, and improve production efficiency.
Conclusion
Heat resistant plastic continues to redefine what’s possible in modern engineering. From automotive innovation to advanced manufacturing, these materials combine lightweight design with remarkable endurance — outperforming traditional materials in many applications.
As industries move toward sustainability and efficiency, the demand for heat resistant engineering plastics will only grow. Choosing the right polymer and temperature control system today means ensuring long-term reliability and performance tomorrow.

Marketing Section: Partner with CNTOPower
At CNTOPower, we specialize in Hot Runner Temperature Controllers and Mold Temperature Control Systems that help manufacturers achieve perfect temperature precision — essential for molding heat resistant plastics.
Key Advantages:
Multi-zone temperature management for precise control
Compatibility with DME, YUDO, and HUSKY standards
Custom configurations for complex molds
Improved energy efficiency and reduced downtime
If you are producing parts from heat resistant plastic materials, CNTOPower can help you reach new levels of consistency, efficiency, and reliability.
Visit: https://www.cntopower.com/HotRunnerTemperatureController/
and discover how our smart temperature control technology can optimize your production.